Java Number & Math 类
一般地,当需要使用数字的时候,我们通常使用内置数据类型,如:byte、int、long、double 等。
实例
1 | int a = 5000; |
然而,在实际开发过程中,我们经常会遇到需要使用对象,而不是内置数据类型的情形。为了解决这个问题,Java 语言为每一个内置数据类型提供了对应的包装类。
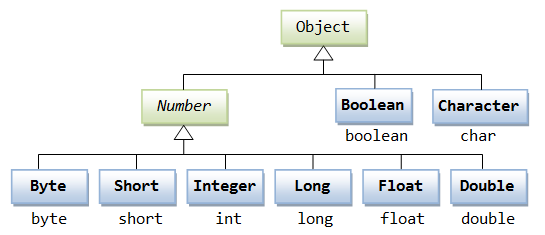
所有的包装类(Integer、Long、Byte、Double、Float、Short)都是抽象类 Number 的子类。
| 包装类 | 基本数据类型 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | boolean |
| Byte | byte |
| Short | short |
| Integer | int |
| Long | long |
| Character | char |
| Float | float |
| Double | double |
这种由编译器特别支持的包装称为装箱,所以当内置数据类型被当作对象使用的时候,编译器会把内置类型装箱为包装类。相似的,编译器也可以把一个对象拆箱为内置类型。Number 类属于 java.lang 包。
下面是一个使用 Integer 对象的实例:
Test.java 文件代码:
1 | public class Test{ |
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
1 | 15 |
当 x 被赋为整型值时,由于x是一个对象,所以编译器要对x进行装箱。然后,为了使x能进行加运算,所以要对x进行拆箱。
Java Math 类
Java 的 Math 包含了用于执行基本数学运算的属性和方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
Math 的方法都被定义为 static 形式,通过 Math 类可以在主函数中直接调用。
Test.java 文件代码:
1 | public class Test { |
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
1 | 90 度的正弦值:1.0 |
Number & Math 类方法
下面的表中列出的是 Number & Math 类常用的一些方法:
| 序号 | 方法与描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | xxxValue() 将 Number 对象转换为xxx数据类型的值并返回。 |
| 2 | compareTo() 将number对象与参数比较。 |
| 3 | equals() 判断number对象是否与参数相等。 |
| 4 | valueOf() 返回一个 Number 对象指定的内置数据类型 |
| 5 | toString() 以字符串形式返回值。 |
| 6 | parseInt() 将字符串解析为int类型。 |
| 7 | abs() 返回参数的绝对值。 |
| 8 | ceil() 返回大于等于( >= )给定参数的的最小整数,类型为双精度浮点型。 |
| 9 | floor() 返回小于等于(<=)给定参数的最大整数 。 |
| 10 | rint() 返回与参数最接近的整数。返回类型为double。 |
| 11 | round() 它表示四舍五入,算法为 Math.floor(x+0.5),即将原来的数字加上 0.5 后再向下取整,所以,Math.round(11.5) 的结果为12,Math.round(-11.5) 的结果为-11。 |
| 12 | min() 返回两个参数中的最小值。 |
| 13 | max() 返回两个参数中的最大值。 |
| 14 | exp() 返回自然数底数e的参数次方。 |
| 15 | log() 返回参数的自然数底数的对数值。 |
| 16 | pow() 返回第一个参数的第二个参数次方。 |
| 17 | sqrt() 求参数的算术平方根。 |
| 18 | sin() 求指定double类型参数的正弦值。 |
| 19 | cos() 求指定double类型参数的余弦值。 |
| 20 | tan() 求指定double类型参数的正切值。 |
| 21 | asin() 求指定double类型参数的反正弦值。 |
| 22 | acos() 求指定double类型参数的反余弦值。 |
| 23 | atan() 求指定double类型参数的反正切值。 |
| 24 | atan2() 将笛卡尔坐标转换为极坐标,并返回极坐标的角度值。 |
| 25 | toDegrees() 将参数转化为角度。 |
| 26 | toRadians() 将角度转换为弧度。 |
| 27 | random() 返回一个随机数。 |
Math 的 floor,round 和 ceil 方法实例比较
| 参数 | Math.floor | Math.round | Math.ceil |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1.5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1.6 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| -1.4 | -2 | -1 | -1 |
| -1.5 | -2 | -1 | -1 |
| -1.6 | -2 | -2 | -1 |
floor,round 和 ceil 实例:
1 | public class Main { |
以上实例执行输出结果为:
1 | Math.floor(1.4)=1.0 |
Java xxxValue() 方法
xxxValue() 方法用于将 Number 对象转换为 xxx 数据类型的值并返回。
相关的方法有:
| 类型 | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| byte | byteValue() :以 byte 形式返回指定的数值。 |
| abstract double | doubleValue() :以 double 形式返回指定的数值。 |
| abstract float | floatValue() :以 float 形式返回指定的数值。 |
| abstract int | intValue() :以 int 形式返回指定的数值。 |
| abstract long | longValue() :以 long 形式返回指定的数值。 |
| short | shortValue() :以 short 形式返回指定的数值。 |
参数
以上各函数不接受任何的参数。
返回值
转换为 xxx 类型后该对象表示的数值。
实例
Test.java 文件
1 | public class Test{ |
编译以上程序,输出结果为:
1 | 5 |
Java compareTo() 方法
compareTo() 方法用于将 Number 对象与方法的参数进行比较。可用于比较 Byte, Long, Integer等。
该方法用于两个相同数据类型的比较,两个不同类型的数据不能用此方法来比较。
语法
1 | public int compareTo( NumberSubClass referenceName ) |
参数
referenceName – 可以是一个 Byte, Double, Integer, Float, Long 或 Short 类型的参数。
返回值
- 如果指定的数与参数相等返回0。
- 如果指定的数小于参数返回 -1。
- 如果指定的数大于参数返回 1。
实例
1 | public class Test{ |
编译以上程序,输出结果为:
1 | 1 |
Java equals() 方法
equals() 方法用于判断 Number 对象与方法的参数进是否相等。
语法
1 | public boolean equals(Object o) |
参数
o – 任何对象。
返回值
如 Number 对象不为 Null,且与方法的参数类型与数值都相等返回 True,否则返回 False。
Double 和 Float 对象还有一些额外的条件,可以参阅 API 手册:JDK 1.6。
实例
实例
1 | public class Test{ |
编译以上程序,输出结果为:
1 | false |