这里则介绍图的另外一种存储方式:邻接矩阵。参考资料《大话数据结构》《C算法:卷二》
一、图的数据结构
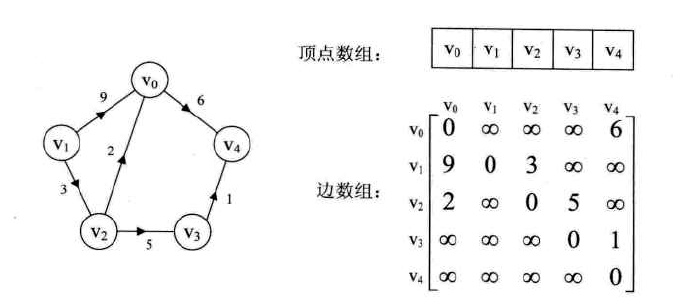
图的邻接矩阵存储方式是用两个数据来表示。一个一维数组存储图中顶点信息,一个二维数组(称为邻接矩阵)存储图中的边的信息。
见下图:(图片来源于《大话数据结构》)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef int VertexType;
typedef int EdgeType;
#define MAXVEX 100
#define INFI 65535
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX];
EdgeType matrix[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
unsigned int numVertexes;
unsigned int numEdges;
}Graph;
|
二、创建一个图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
Graph* CreateGraph()
{
Graph *pGragh = new Graph;
if (NULL == pGragh)
return NULL;
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> pGragh->numVertexes >> pGragh->numEdges;
for (int i = 0; i < pGragh->numVertexes; ++i)
(pGragh->vexs)[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < pGragh->numVertexes; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < pGragh->numVertexes; ++j)
{
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = INFI;
if (i == j)
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < pGragh->numEdges; ++k)
{
int i, j, w;
cout << "输入边(vi,vj)上的下标i,下标j和权重w:" << endl;
cin >> i >> j >> w;
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = w;
(pGragh->matrix)[j][i] = (pGragh->matrix)[i][j];
}
return pGragh;
}
Graph* CreateDiGraph()
{
Graph *pGragh = new Graph;
if (NULL == pGragh)
return NULL;
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> pGragh->numVertexes >> pGragh->numEdges;
for (int i = 0; i < pGragh->numVertexes; ++i)
(pGragh->vexs)[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < pGragh->numVertexes; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < pGragh->numVertexes; ++j)
{
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = INFI;
if (i == j)
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < pGragh->numEdges; ++k)
{
int i, j, w;
cout << "输入边<vi,vj>上的下标i,下标j和权重w:" << endl;
cin >> i >> j >> w;
(pGragh->matrix)[i][j] = w;
}
return pGragh;
}
|
三、检查图中两个顶点间是否有边
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
bool GraphHasEdge(Graph *pGraph, unsigned int begin, unsigned int end)
{
if (NULL == pGraph || begin >= pGraph->numVertexes || end >= pGraph->numVertexes)
return false;
if (begin == end)
return false;
return ((pGraph->matrix)[begin][end] != INFI) ? true : false;
}
|
四、DFS
关于DFS与BFS的介绍见开篇链接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
void DFSUtil(Graph *pGraph, int start, bool visited[])
{
visited[start] = true;
cout << start << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < pGraph->numVertexes; ++j)
{
if ((pGraph->matrix)[start][j] != 0 && (pGraph->matrix)[start][j] != INFI && !visited[j])
DFSUtil(pGraph, j, visited);
}
}
void DFS(Graph *pGraph)
{
if (NULL == pGraph)
return;
bool *visited = new bool[pGraph->numVertexes];
memset(visited, false, pGraph->numVertexes);
for (int i = 0; i < pGraph->numVertexes; ++i)
{
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(pGraph, i, visited);
}
delete[] visited;
}
|
五、BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
void BFS(Graph *pGraph)
{
if (NULL == pGraph)
return;
bool *visited = new bool[pGraph->numVertexes];
memset(visited, false, pGraph->numVertexes);
list<int> queue;
for (int i = 0; i < pGraph->numVertexes; ++i)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
visited[i] = true;
cout << pGraph->vexs[i] << endl;
queue.push_back(i);
while (!queue.empty())
{
i = *queue.begin();
queue.pop_front();
for (int j = 0; j < pGraph->numVertexes; ++j)
{
if ((pGraph->matrix)[i][j] != 0 && (pGraph->matrix)[i][j] != INFI && !visited[j])
{
visited[j] = true;
cout << pGraph->vexs[j] << endl;
queue.push_back(j);
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
这里只提供相关代码实现,代码已测试,理论部分请参考相关资料。